Reducing On-Farm Food Losses
In the OIC Member Countries
7
However, many times an activity or practice undertaken during production can lead directly to
food losses at the moment of harvest and further down the value chain, such as when crops or
animals do not receive adequate nutrition, are not protected from known pests (i.e. insects or
weeds), or suffer sun-burn or wind damage. FAO and the SAVE FOOD Initiative (2015, as yet
unpublished) have recently updated their definitions of food losses to include intentional or
unintentional pre-harvest losses. These updated definitions for food losses will be used in all
FAO programmes going forward. In the new definition, pre-harvest losses are included in the
production stage, and harvesting has been moved into the category of postharvest losses. The
details will be found in the FAO (in press at the time of this report). Table 1.1 summarizes the
variety of definitions available.
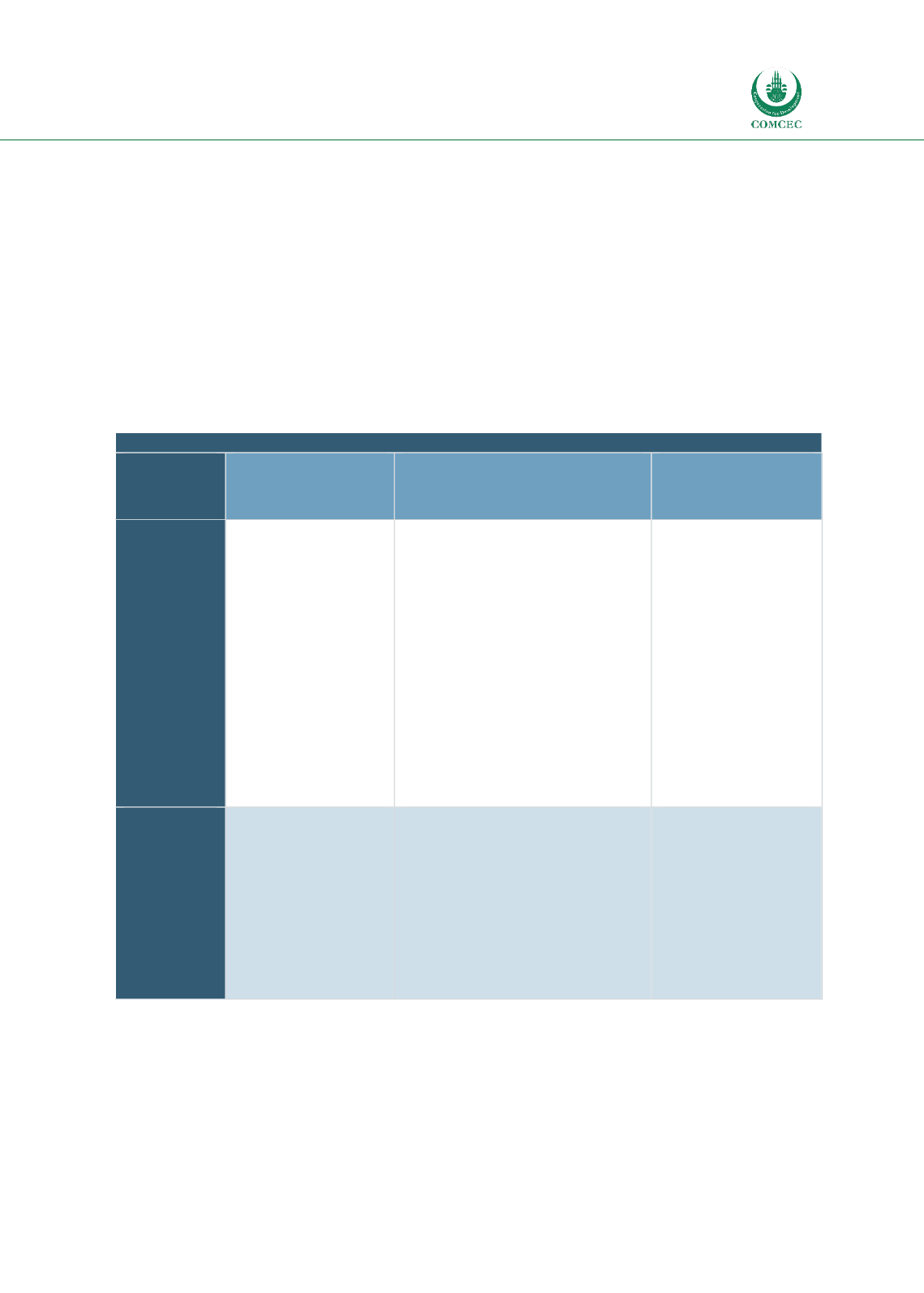
Table 1.1: Varying Definitions of Food Losses in Use and Under Development
Varying Definitions
Sources
FAO (Gustavsson
2011; SIK 2013)
WRI (Lipinski et al 2013; Food
loss and waste protocol, on-going
as of 2015)
SAVE FOOD Initiative
(2015)
On-Farm
Losses
Any losses in the
agricultural
production stage
until completion of
harvesting
Losses during production or
harvest in the form of foods left
behind by poor harvesting
equipment, discarded or not
harvested or discarded because
they fail to meet quality standards
or are uneconomical to harvest.
Losses during
production, including
food that is fit to
enter the food supply
chain (FSC), but
intentionally
discarded or
redirected to non-
food use in the pre-
harvest phase; and
food that is harvest-
mature and
unintentionally
getting spoilt in the
pre-harvest phase.
Postharvest
Losses
Food damage or
degradation of food
during the different
stages such as
handling, storage,
processing,
packaging, and
distribution to the
moment of final
consumption
Losses during handling and
storage in the form of food
degraded by pests, fungus, and
disease, and losses during
processing and packaging in the
form of spilled milk, damaged fish,
and foods unsuitable for
processing.
Losses during
harvesting and
handling
Losses during storage
Losses during
processing, packaging
and distribution