Improving Institutional Capacity:
Strengthening Farmer Organizations in the OIC Member Countries
63
4.2.2.
Actors working to strengthen FOs and their activities
Numerous multilateral agencies, bilateral agencies, NGOs and private sector organizations
have been actively involved in strengthening FOs according to the strategies described in Table
21 above, through direct engagement, grassroots capacity building, advocacy and policy-
related interventions, or by providing means for training. IFAD, the World Bank, FAO, African
Development Bank (AfDB), European Bank for Reconstruction and Development (EBRD),
Asian Development Bank (ADB), and others have contributed across all avenues listed above,
especially over the past four years. Germany’s Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit
(GIZ), the United States Agency for International Development (USAID), and more bilateral
donors contribute in a similar nature, while agencies specifically mandated for co-operative
development, such as the International Labor Organization (ILO), have created extensive
cooperative development networks and legal frameworks. Below, Figure 13 describes the
common activities these organizations engage in as they attempt to strengthen farmer
organizations.
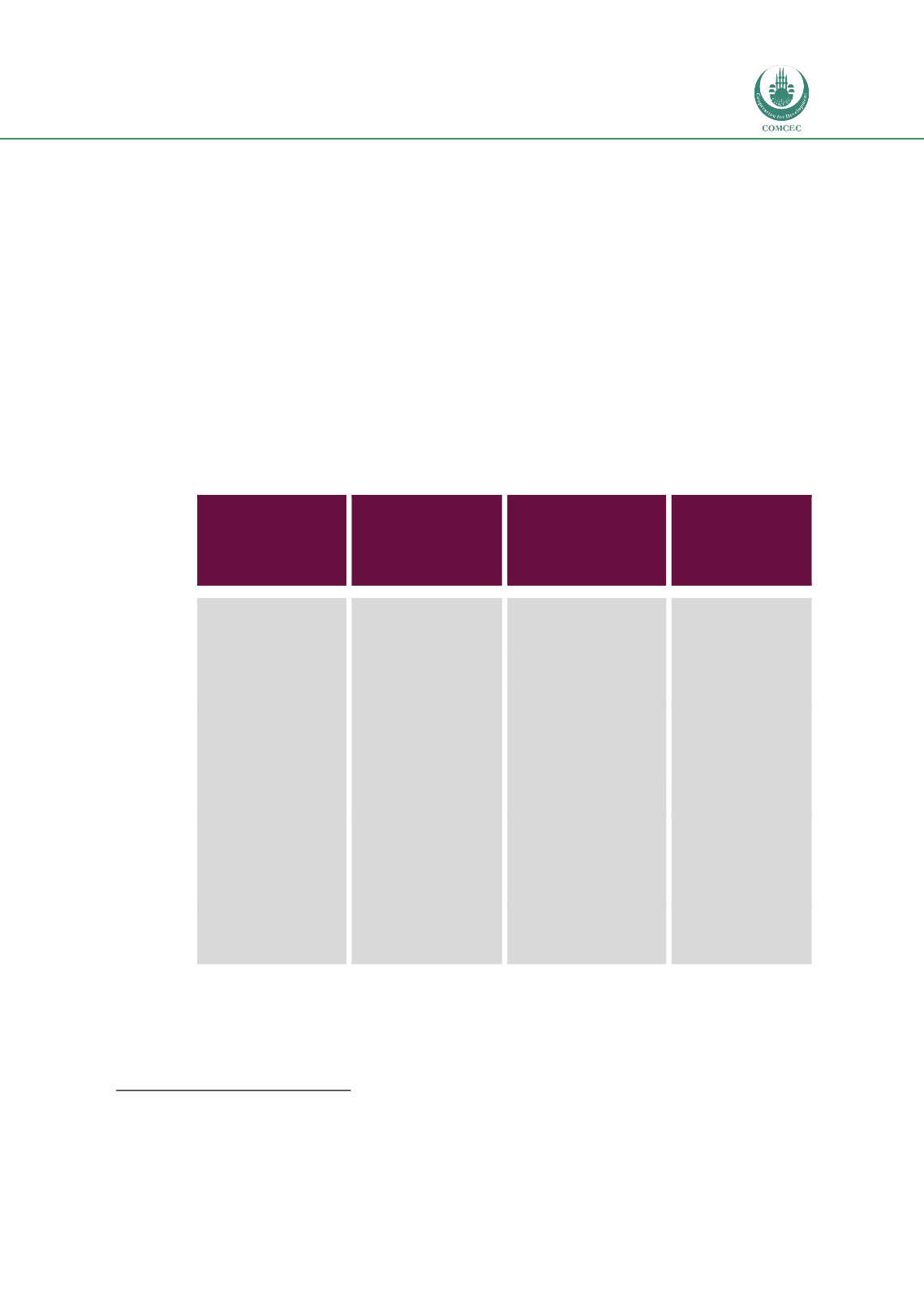
Figure 14: Common FO-supporting activities of bilateral and multilateral agencies
89
Activities
Invest in
strengthening
service providers
Invest in training and
development models
for FO networks
Build evidence base
and identify lessons
learned
Amplify the “Voice
of the Farmer”
(VoF) and build
feedback into
partnerships
Supporting
Initiatives
Pilot service
provider network to
share best practices
Support networks of
FOs in on-job
training, in business
skills, governance
and accountability
mechanisms
Identify lessons
learned and best
practices in effective
FO partnerships and
disseminate across
countries externally
Develop and pilot
approaches /
mechanisms for
eliciting the voice
of the farmer
Upgrade facilities
and FO-focused
curriculum of select
Colleges, Technical &
Vocational centers
Establish and
support linkages
between FOs and
academic research
and Ag advisory
services
Develop typology of
FO models and
diagnostic tool to
measure impact of FOs
Synthesize and
share the VoF with
key stakeholders,
including donors
and public
agencies
Build capacity of
public agencies with
responsibility for
cooperatives and FOs
Identify and
promulgate models
that are more / less
effective for FO skill
development
Develop empirical
research-based FO
case studies in
representative
countries
Develop process
for incorporating
VoF into impact
evaluations of
programs
Identify implications
for optimal legal &
policy environment
Significant actors and their initiatives and programmes are highlighted below. Most fall into
two broad categories: (i) agencies with an agricultural development bent, and (ii) agencies that
generally promote cooperative labor models. Below, some of the leading actors and examples
of their strategies and recent work are examined.
89
This figure is drawn from Dalberg experience in supporting international actors focused on farmer organization
development