Reviewing Agricultural Trade Policies
To Promote Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
170
referenced international databases that collect and publish statistics on tariff rates and NTMs at
product division and product levels do not cover the statistics of most recent years for many OIC
countries.
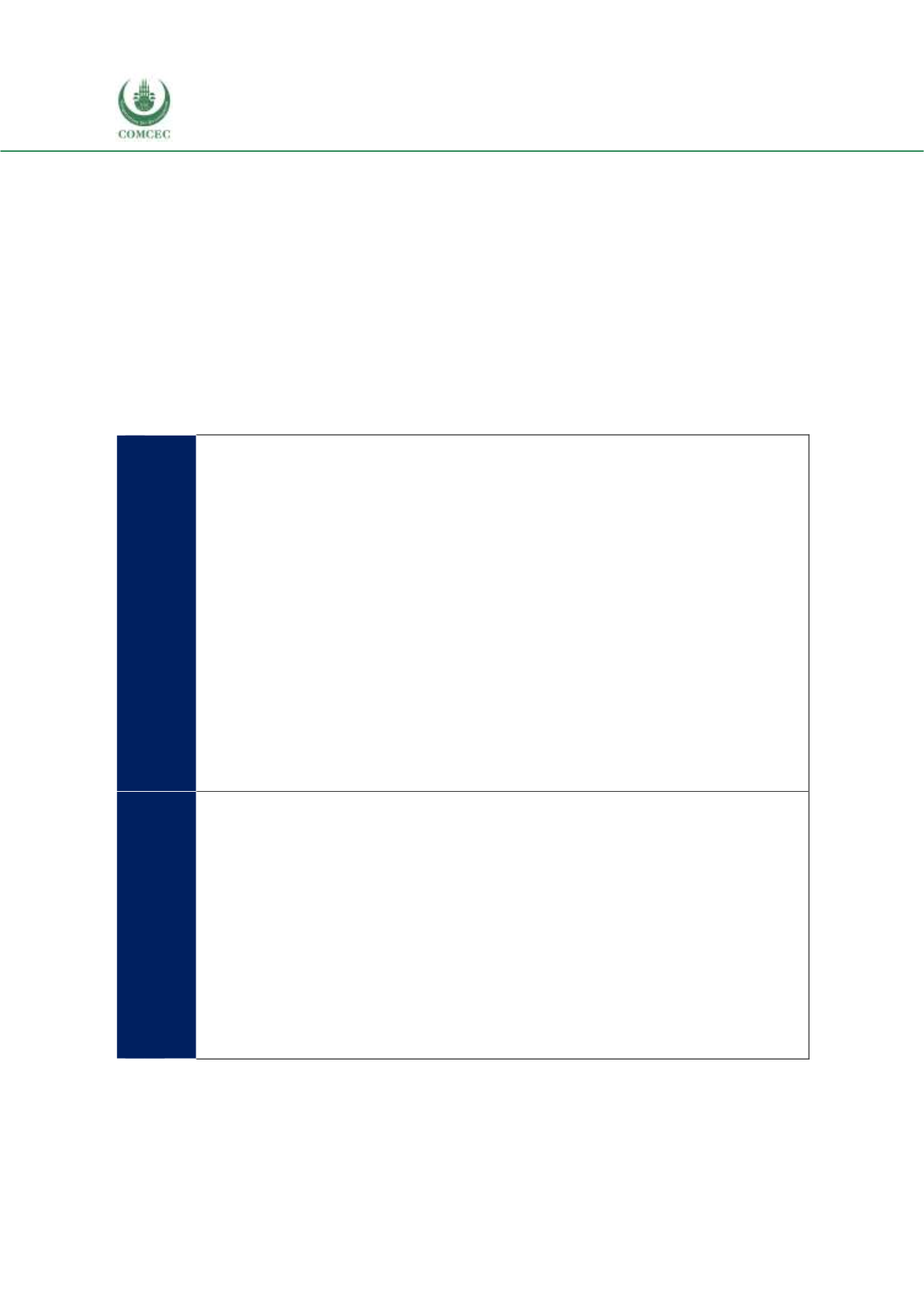
5.2. A SWOT Analysis of Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
Before proceeding to the emerging policy recommendations, a summary table of the SWOT
analysis that has been carried out for intra-OIC trade in agricultural products is presented in this
subsection. Trade promotion for a particular group of countries and products is a multi-faceted
phenomenon at both extensive and intensive margins of trade. The design and implementation
of effective agricultural trade policies through tariff measures, NTMs, and trade agreements are
processes that should be complemented with policies that target the structural micro and macro
problems for individual countries and for the group as a whole.
Table 5. 1 SWOT Analysis for Intra-OIC Agricultural Trade
General
Strengths
Members globally ranking among the top 20 producers of many agricultural
products
Non-satiated domestic markets and increasing domestic demand for food
Suitable climate for agricultural production in most OIC members
Weaknesses
Low value added in exports (unprocessed/raw or semi-processed)
Lack of insurance mechanisms against production and marketing risks
Opportunities
Not fully tapped export markets for many agricultural products
Threats
Low overall level of development of member economies
Political conflicts
Climate change
Similarity of the geography and factor endowments across countries
Poor renewable water resource endowments of many members
Production
(General)
Strengths
Young population
Vast (but unevenly distributed) stock of arable lands
Wide range of product variety
Weaknesses
Fragmented lands and scale problems
Generally low level of agricultural productivity
Poorly educated labor force
Low capacity to control the effects of weather on agricultural production
Threats
Climate change
Increasing oil prices (for members that are net importers)