
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
119
development, international collaborations, industry linkages, and, most importantly, they will
attract private investments for ensuring the sustainability of the initiative.
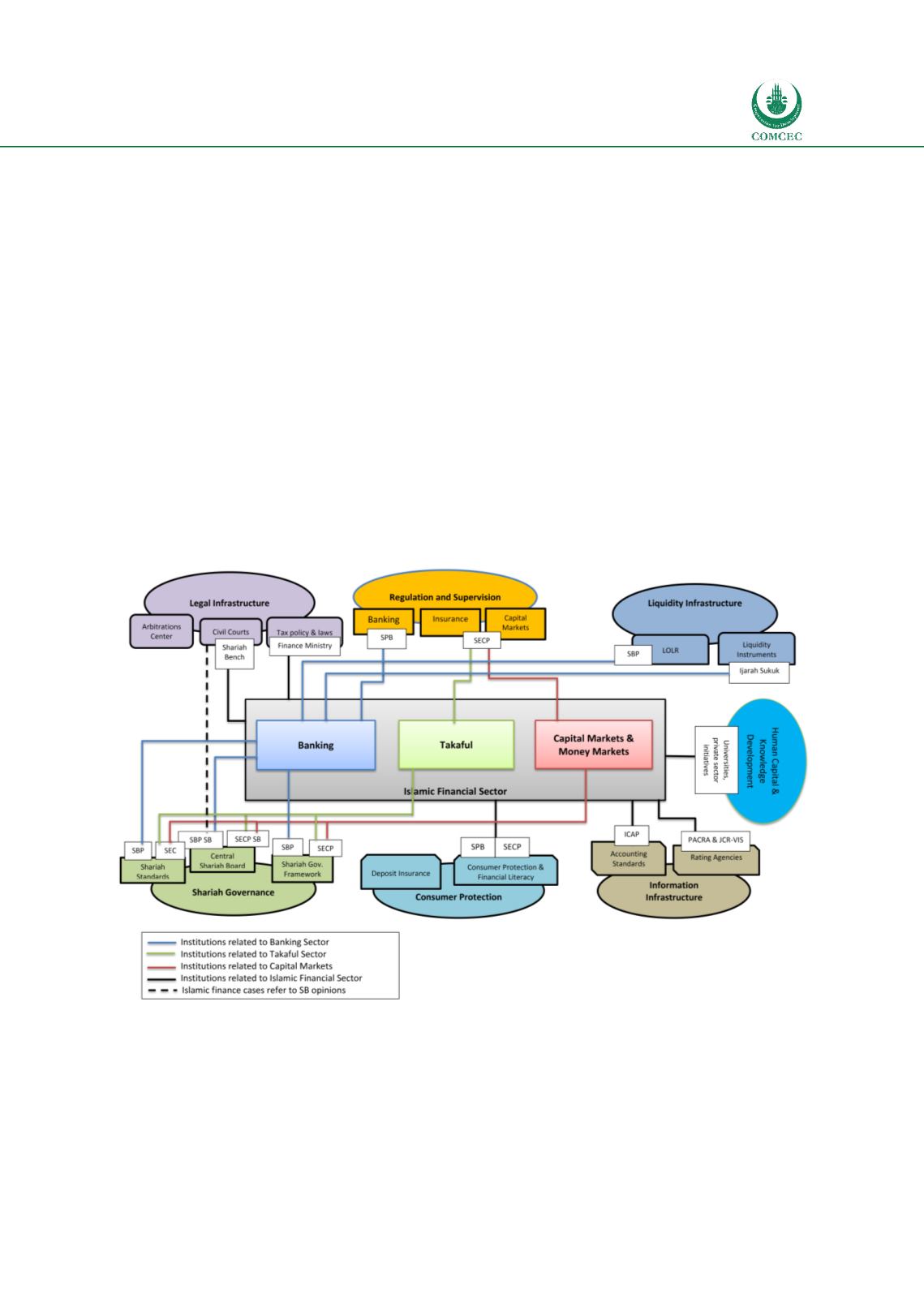
4.7.8. Summary and Conclusions
A comprehensive regulatory and supervisory framework has been provided to the Islamic
financial institutions in Pakistan with focus to ensure Shariah compliance. The Shariah
Governance Framework ensures Shariah compliance, improving transparency and bringing
standardization in the IBIs’ practices while taking care for stability of the system. The areas
where efforts need to be put in are providing special laws and regulation, and tax neutrality
facilitating the IBIs to undertake business in line with the Shariah principles in letter and spirit.
Currently there is no code of conduct for banks in Pakistan. SBP's (2009) 10-year strategy has
planned to encourage the Pakistan Banks’ Association (PBA) to adopt a Banking Code of Ethics,
which could be used as a basis for committing all banks to fairness, disclosure, and proper
ethical standards. Generally sound grievance and redress mechanisms exist in Pakistan for
bank customers, but their effectiveness could be enhanced by increasing awareness of the
process and streamlining procedures. The government and the regulators also need to take
care of the social and distributive impacts of the banking and monetary practices.
Chart
4.7: Islamic Financial Architecture Institutions—Pakistan
















