
National and Global Islamic Financial Architecture:
Prolems and Possible Solutions for the OIC Member Countries
109
4.6.8. Summary and Conclusions
Although Oman started late in offering Islamic Banking and Takaful compared to other Gulf
Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, it is has a good start with a sound infrastructure. It has
an advantage from the experience of GCC countries and their practices in Islamic finance. The
government has shown an interest and given support to it during last three years that has
resulted in rapid growth of the sector in the country. The legal and regulatory infrastructure
for Islamic finance includes laws and regulations for Islamic banks, takaful companies and the
Islamic capital market. In addition, the Central Bank of Oman (CBO) currently is working on an
insurance scheme for depositors of Islamic banking and the Capital Market Authority (CMA)
has prepared Sukuk Regulation which is in its final stage of approval. Also, there is a High
Sharia Supervisory Authority (HSSA) which provides opinions and expert advice on Sharia
matters to the CBO. The government of Oman has shown interest for continuous development
of Islamic financial institutions and markets both on the demand and supply sides. Other than
laws and regulation to support the industry, it has sponsored different training programs and
hosted different conferences to raise awareness of the public. Along with government
initiatives, Islamic banks and widows are also contributing to different educational events such
as conferences, seminars and training programs to raise an awareness of Islamic banking and
finance in the country.
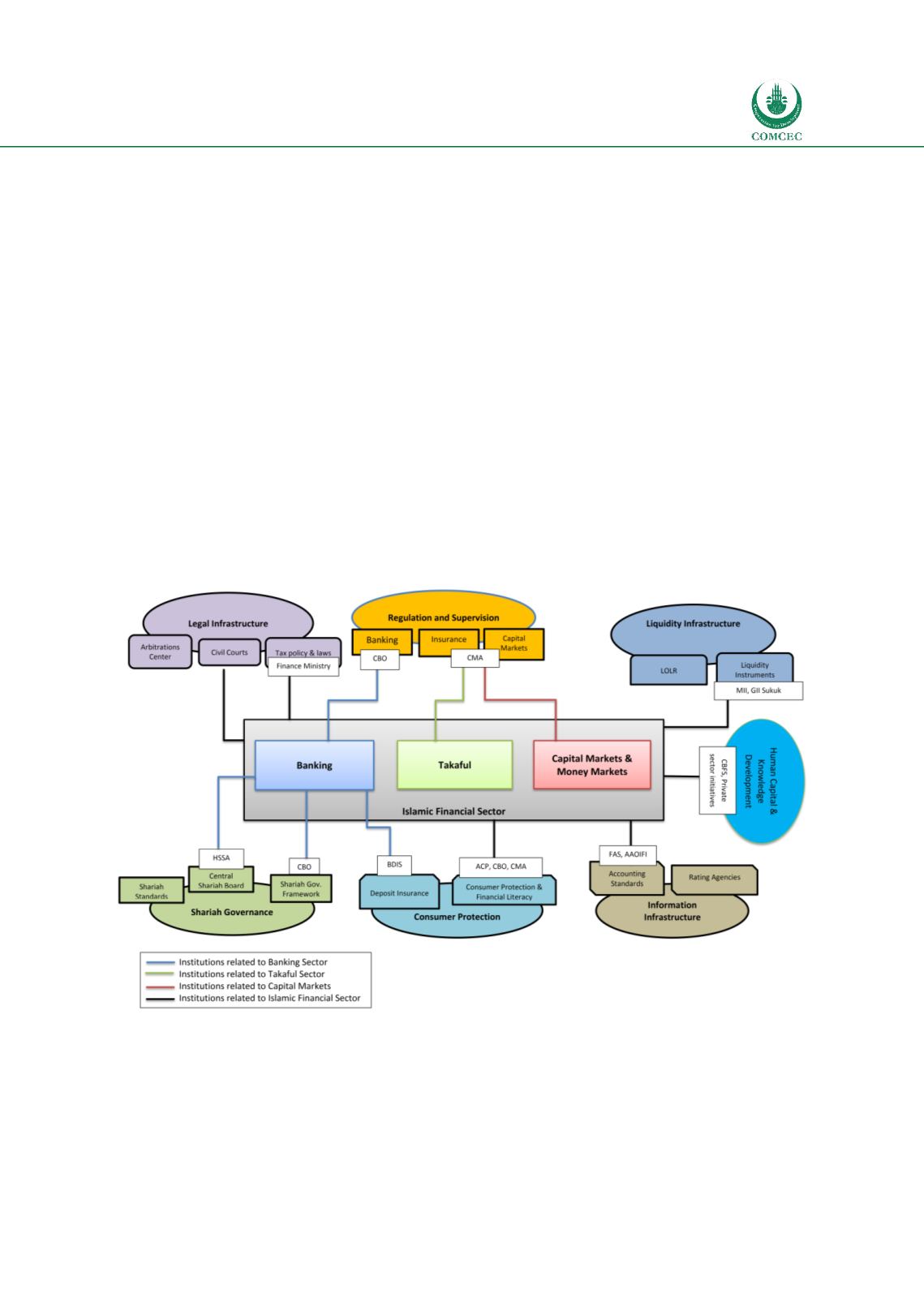
Chart
4.6: Islamic Financial Architecture Institutions—Oman
















