4
In addition to compliance to the international standards, border agency cooperation (BAC) is another
important aspect of trade facilitation in global agenda. According to the WTO Trade Facilitation
Agreement, which was also signed by 15 OIC Member Countries, the concerned countries committed
to cooperate in the following issues regarding cross border
cooperation:
alignment of working days and hours,
alignment of procedures and formalities
development and sharing of common
facilities
joint controls
establishment of one stop border post
control
The level of border agency cooperation of the OIC Member
Countries varies according to the several indices measuring
the countries’ level of border agency cooperation.
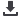
According to World Bank’s Logistics Performance Index
(LPI), which measures the efficiency of the clearance
process scaling from 0 to 5, the Asian Group countries have
the highest average score of 2.53 in the efficiency of the
clearance processes, followed by the Arab Group Countries
with the score of 2.46. On the other hand, African Group
Countries have the lowest average with the score of 2.30.
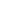
Moreover, OECD External Border Agency Cooperation (BAC) Indicator, scaling from 0 to 2, measures
the border agency cooperation with neighbouring and third countries. Accordingly, the average of
external cooperation for the Arab Group is 1.15, followed by the Asian and African Group countries
with the score of 1.11 and 0.82, respectively.
Considering the importance of BAC for trade facilitation as well as increasing intra-OIC trade, the 8
th
Meeting of the COMCEC Trade Working Group held on October 6
th
, 2016, was devoted to “Improving
the Border Agency Cooperation among the OIC Member States for Facilitating Trade.” The research
study and the participants of the working group highlighted the major challenges faced by the Member
Countries, among others:
Lack of coordination and cooperation among border agencies
Long, costly and inefficient customs procedures
Lack of harmonized working hours among the countries
Inadequate information exchange among the border agencies