Improving the Border Agency Cooperation
Among the OIC Member States for Facilitating Trade
55
In the field of trade cooperation, there have been important achievements such as adopting
several laws and regulations, enhancing economic citizenship, and setting up mutual
commissions. Efforts are geared towards converting a number of reference trade laws and
regulations into binding GCC laws. Other new draft laws are being concluded, including the
Common Trade law, Unified law of Commercial Agencies, Common Commercial Registration
Law, GCC Commercial Fraud Control, GCC Consumer Protection law, GCC Competition Law,
GCC Commercial Secrets Law, Unified Law for Supervision and Control of Insurance Activities,
Unified Law of Auditing and Common Electronic Transactions law.
The GCC demonstrates advanced collaborative arrangements between customs
administrations under the GCC Customs Union that was established in 2003 and has been
operational since 2015. The Customs Union demonstrates many forms of cooperation, such as
a single entry point system for imported goods, common customs regulations and procedures,
common rules for calculation of customs value of foreign goods, and so forth. In addition, there
are provisions for sharing customs expertise through the exchange of customs officers and
through common training programs.
82
Other regional initiatives
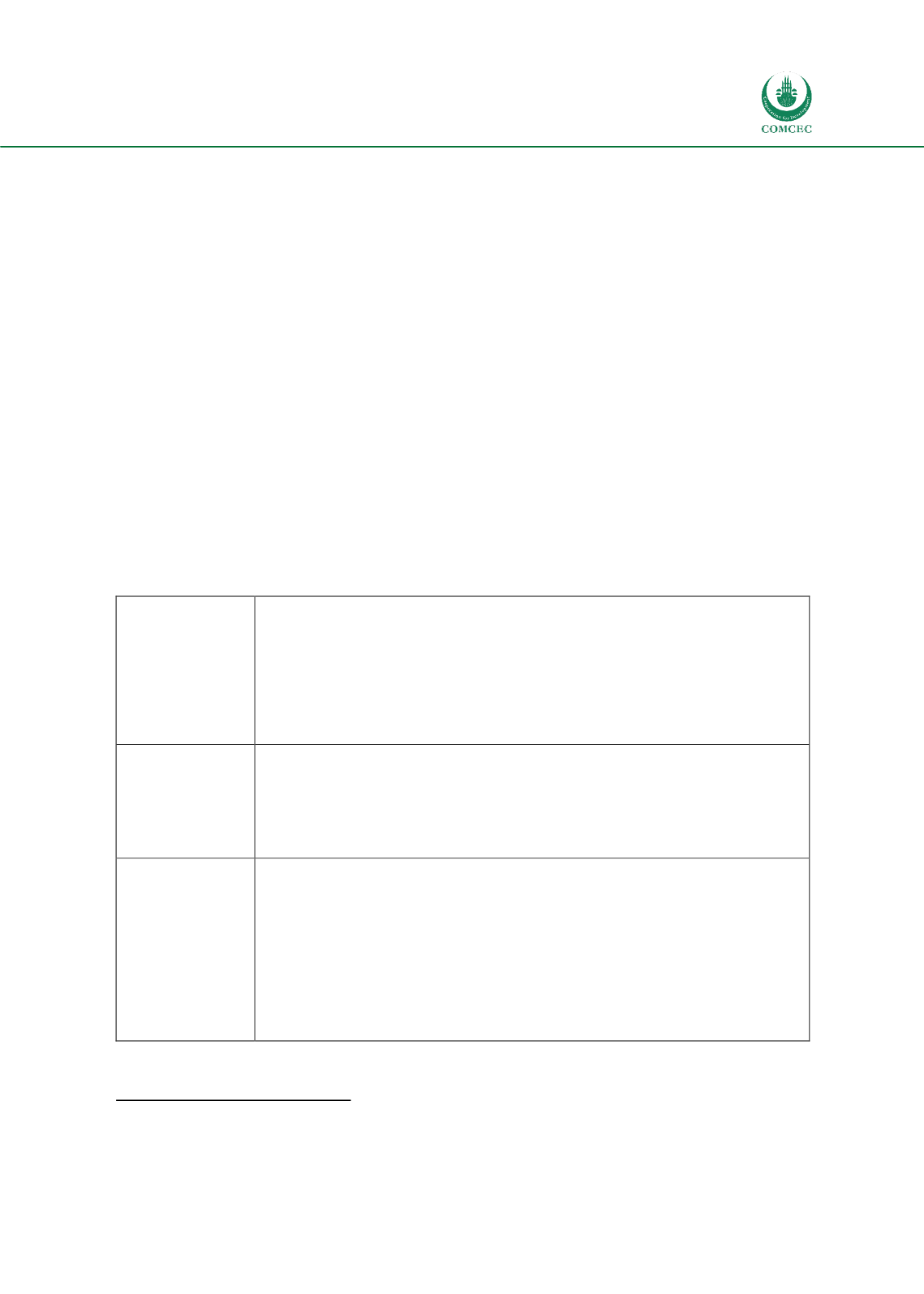
Table 5. Other regional initiatives in Arab region
The Arab
Maghreb Union
The Conseil Permanent Consultatif du Maghreb (CPCM) was established in 1964
between the five Maghreb states Algeria, Libya, Mauritania, Morocco, and Tunisia,
which are all OIC member states. The main objective was to coordinate and
harmonise the development plans of the five countries and foster interregional trade
and relations with the EU. Since this is essentially a trade agreement, customs
cooperation is a key element for increasing the effectiveness of customs controls and
facilitating trade. However, at this stage it is not possible to indicate the exact
dynamics of BAC due to unsatisfactory progress in the integration process.
Council of Arab
Economic Unity
The Council of Arab Economic Unity (CAEU) is an economic organisation that was
established in June 1957. As the name suggests, the focus of this organisation,
economic integration, is to be achieved within a framework of economic and social
development to promote freedom of movement for labor, capital, and services. Today,
the members include 12 OIC countries, namely Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Kuwait, Libya,
Mauritania, Palestine, Somalia, Sudan, Syria, the UAE, and Yemen.
Common Market
for Eastern and
Southern Africa
The main focus of the Common Market for Eastern and Southern Africa (COMESA) is
on the formation of a large economic and trading unit that is strong enough to
overcome several barriers faced by individual states. COMESA forms a major market
hub for both internal and external trading, spanning an impressive geographical area
of 12 million sq. km. Currently it has 19 member states, including six OIC members.
The OIC countries are Comoros, Djibouti, Egypt, Libya, Sudan and Uganda. COMESA
has set itself ambitious goals in a number of areas, and the ultimate objective of
cooperation in trade, customs and monetary affairs is the creation of a fully
integrated, unified single economic space allowing the free movement of goods,
services, capital and labour across national frontiers.
Source: Organization websites and documents
82
The relevance of GCC in BAC-context is explored further in our Abu Dhabi / UAE case study (Chapter 4).