
Improving Public Debt Management
In the OIC Member Countries
13
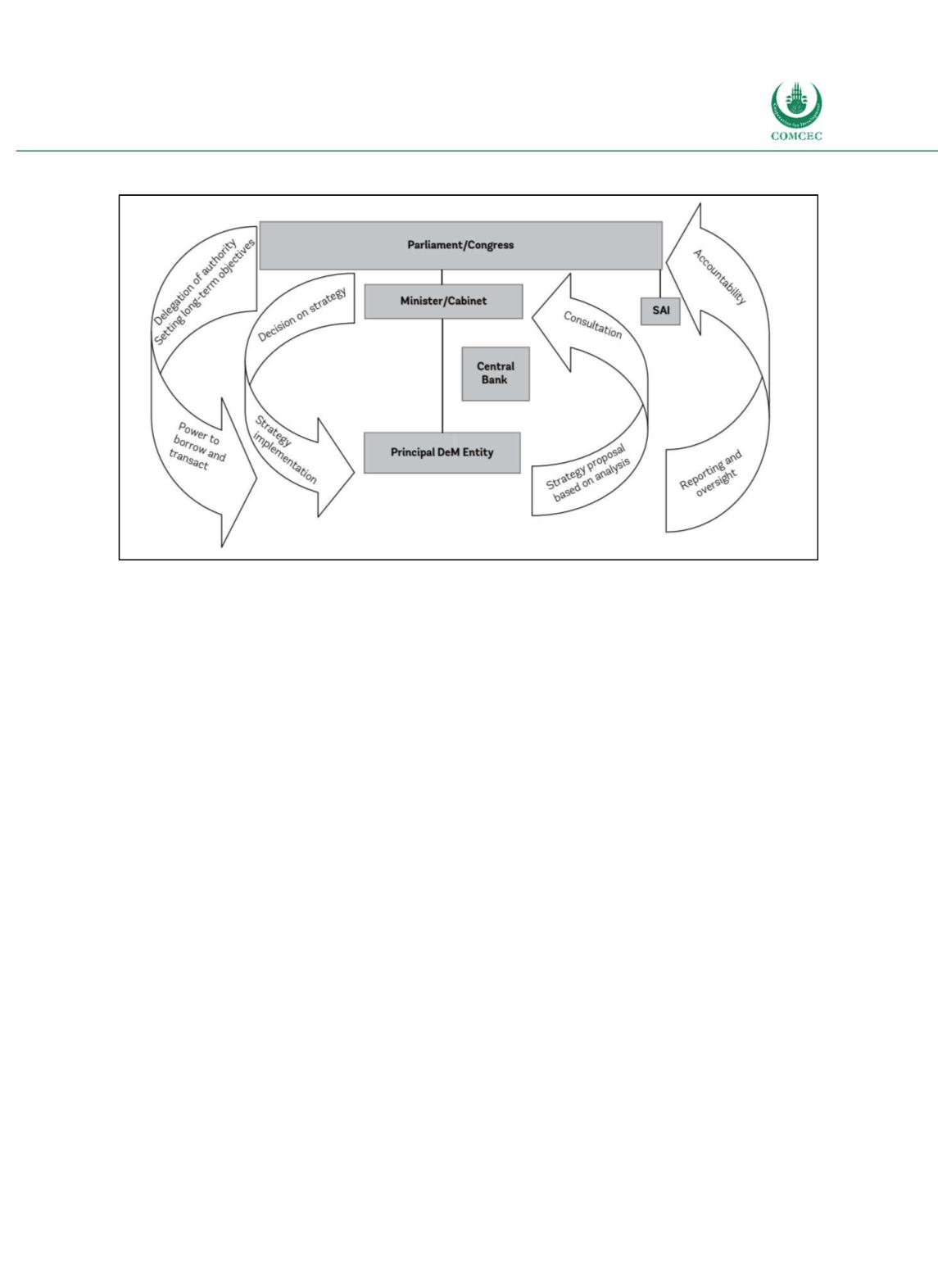
Figure 1-1: Public Debt Management Governance Structure
Note: DeM = Public Debt Management, SAI = Supreme Audit Institution
Source: World Bank (2015, p. 6).
It is advisable that public debt management operations are undertaken by one integrated
principal entity, such as a debt management office (DMO). Only as an alternative if such
integration is not feasible, multiple entities may execute specialized tasks. In that case, all
entities should ensure a regular exchange of information and a clear coordination of their
activities through formal institutional mechanisms. In principal, it proves to be beneficial if the
task of public debt management is assigned to either the national central bank or to the
Ministry of Finance. On one hand, concerns over price stability and a smooth transmission
channel of monetary policy may speak in favor of the central bank. On the other hand, the
pursuit of macroeconomic goals and, in practice most importantly, the minimization of
financing costs for the budget may make the Ministry of Finance the adequate institution for
supervising and conducting debt management operations. Moreover, locating a consolidated
debt management entity within the Ministry of Finance facilitates coordination and
information sharing. For a separate debt management office outside the mentioned
institutions, formal agency arrangements as well as stronger accountability and transparency
frameworks are required (Togo et al. 2003). Finally, debt management tasks may be assigned
to an interagency body. However, given that the Ministry of Finance is the natural authority
responsible for a country’s financial stability, such a body should be chaired by the Ministry of
Finance (Bangura et al. 2000).
Debt management strategy
The legislation should stipulate the debt management entity to develop a debt management
strategy. The strategy defines the objectives for the management of domestic and external
public debt, other financial (contingent) liabilities and related assets. In particular, the debt
management strategy refers to a document that defines target values and benchmarks for risk
indicators of the debt structure. Developing a debt management strategy may provide many
advantages (Cabral 2015), including but not limited to:
















